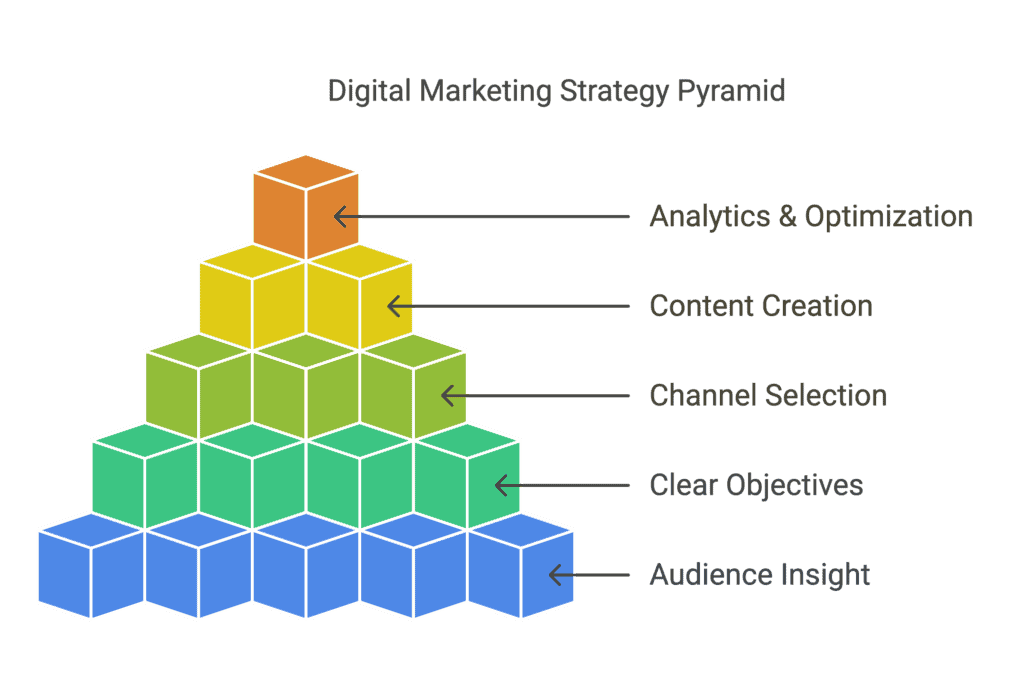
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn the core fundamentals of creating an effective digital marketing strategy that drives real business results. Whether you’re a small business owner just getting started or a marketing professional looking to refine your approach, this resource will help you build a strong foundation.
- Understanding strategy vs. tactics
- Creating effective marketing objectives
- Developing your unique value proposition
- Performing market research
- Building a strong brand framework
- Optimizing customer experience
- Setting up proper analytics
Difference Between A Marketing Strategy and Tactics
Your digital marketing strategy is the master plan that guides all your online marketing efforts. Many businesses fail because they confuse strategy with tactics.
A strategy answers WHY and WHAT you’re trying to accomplish. It’s your high-level game plan that aligns with business objectives.
Tactics are the HOW – the specific actions, channels, and techniques you’ll use to execute your strategy.
For example, “increase brand awareness among millennials” is strategic. “Running Instagram Stories ads” is tactical.
Without a clear strategy, you end up with random acts of marketing – disconnected tactical efforts that drain your budget without delivering consistent results.
Beginner Task: Write down one primary business goal and three supporting marketing objectives that would help achieve that goal.
Advanced Task: Audit your current marketing activities and classify them as either strategic or tactical. Identify any tactics that aren’t clearly connected to strategic objectives and either eliminate them or realign them.
Elements Of A Digital Marketing Strategy
A comprehensive digital marketing strategy contains several crucial components that work together. Getting these foundational elements right makes all the difference between scattered efforts and cohesive marketing.
- Clear business and marketing objectives
- Deep understanding of your target audience
- Unique value proposition
- Defined budget and resource allocation
- Channel selection and prioritization
- Content and messaging framework
- Measurement plan
Let’s explore each of these elements in detail.
Setting SMART Marketing Objectives
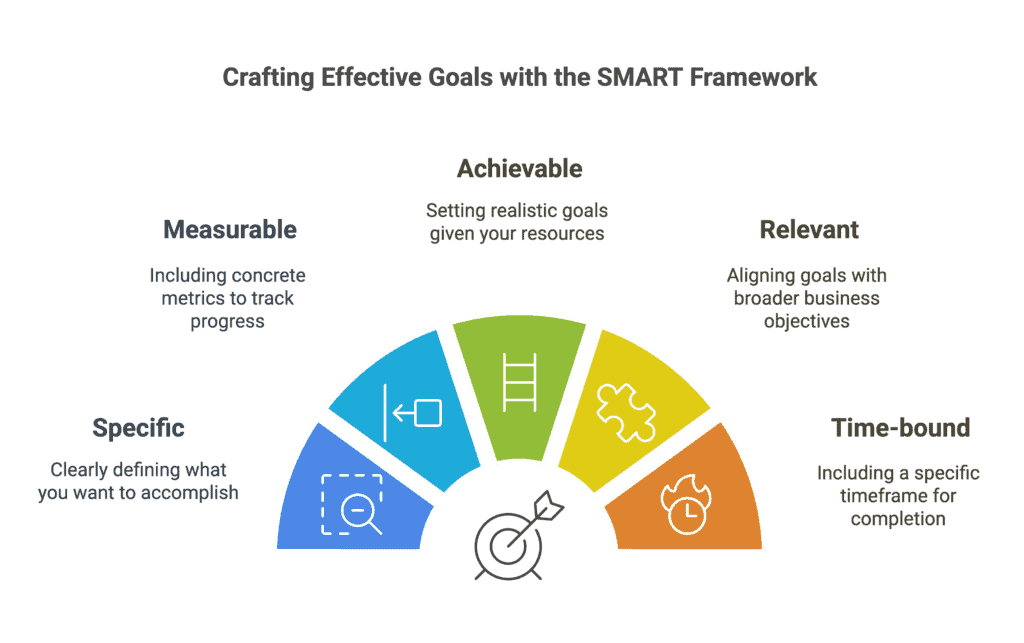
Effective digital marketing starts with setting the right objectives. Vague goals like “increase online presence” aren’t specific enough to guide your efforts or measure success.
Instead, use the SMART framework to create objectives that are:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to accomplish
- Measurable: Include concrete metrics to track progress
- Achievable: Set realistic goals given your resources
- Relevant: Align with broader business objectives
- Time-bound: Include a specific timeframe
For example, instead of “get more website traffic,” a SMART objective would be “increase organic website traffic by 30% within the next 6 months by publishing 12 in-depth guides targeting high-value keywords.”
When your objectives meet these criteria, they provide clear direction and make it easier to determine which tactics deserve your time and budget.
Beginner Task: Take one vague marketing goal you have and rewrite it as a SMART objective, making sure it includes all five elements.
Advanced Task: Create a hierarchy of objectives with 1-2 primary goals and 3-5 supporting sub-objectives. For each, identify the key metrics you’ll track and set up a simple dashboard to monitor progress.
Developing a Unique Value Proposition (UVP)
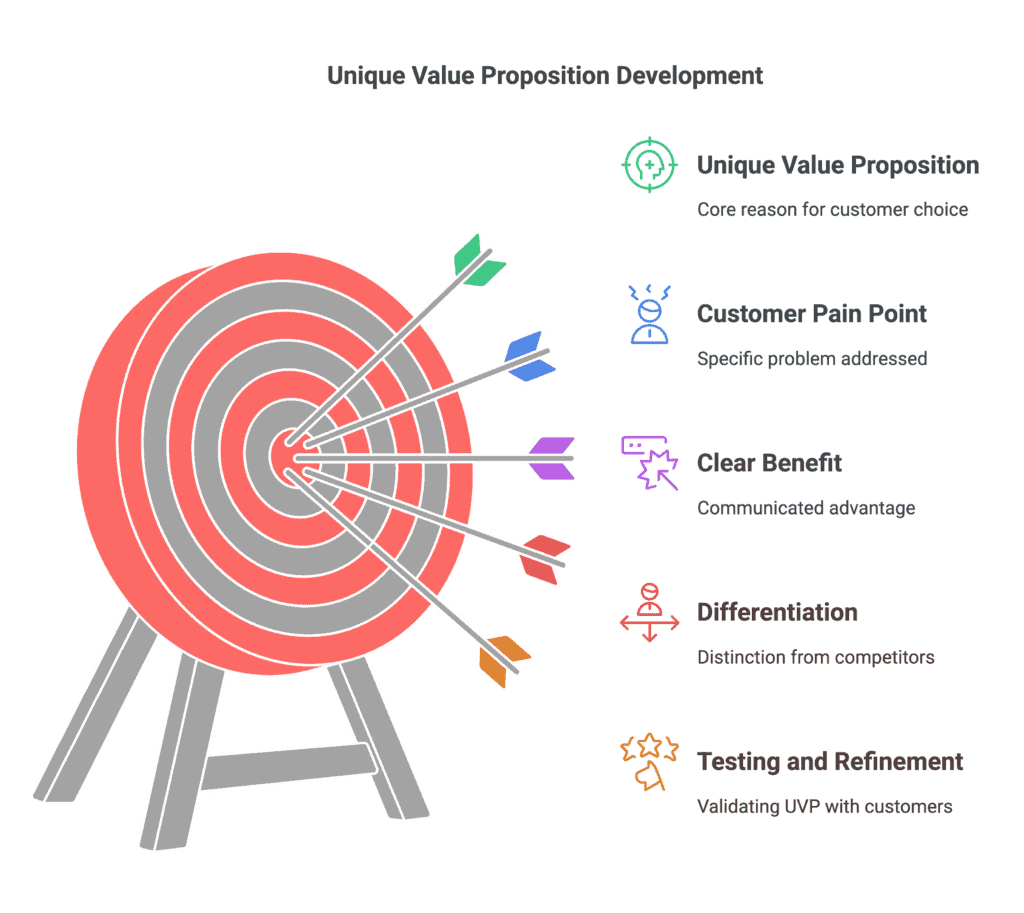
Your Unique Value Proposition is the single most important element of your marketing strategy. It clearly articulates why customers should choose you over competitors.
A strong UVP:
- Addresses a specific customer pain point
- Communicates a clear benefit
- Differentiates you from competitors
- Is concise and easy to understand
- Can be delivered consistently
Too many businesses create generic value propositions like “high-quality products at affordable prices.” This doesn’t tell customers anything meaningful about why they should choose you.
Instead, get specific about the unique value you provide. For example, Stripe’s UVP isn’t just “payment processing” but “payments infrastructure for the internet” that emphasizes developer-friendly tools and simplicity.
Your UVP should influence everything from your website copy to your social media content and email marketing campaigns.
Beginner Task: Identify three specific ways your business solves problems differently than competitors, then craft a simple one-sentence UVP based on your strongest differentiator.
Advanced Task: Test your UVP with actual customers through A/B testing on your landing pages or through customer interviews. Refine based on which version resonates most strongly with your target audience.
Tactical Planning Frameworks
Once you have your strategy in place, you need a systematic approach to planning tactics. Several frameworks can help organize your tactical planning:
The RACE Framework provides a simple structure:
- Reach: Build awareness through SEO, social media, and PR
- Act: Generate leads with compelling content and CTAs
- Convert: Turn prospects into customers with optimized sales funnels
- Engage: Foster loyalty through email, social media, and customer service
Another useful approach is the PESO Model which organizes tactics by channel type:
- Paid Media: Advertising you pay for directly
- Earned Media: PR, mentions, and coverage you earn
- Shared Media: Social platforms where content is shared
- Owned Media: Channels you control like your website and blog
Using these frameworks helps ensure your tactics are balanced across different channels and customer journey stages.
Beginner Task: Choose one framework (RACE or PESO) and categorize your current marketing activities accordingly. Identify any gaps where you’re not utilizing certain stages or channels.
Advanced Task: Create a 90-day tactical roadmap that aligns specific activities with your strategic objectives. Include timelines, owners, budgets, and expected outcomes for each tactic.
Digital Marketing Audit Techniques
Before you can create an effective strategy, you need to understand your current digital marketing performance. A comprehensive audit reveals strengths to leverage and weaknesses to address.
A good digital marketing audit includes:
- Website Performance Analysis: Assess UX, page speed, mobile-friendliness, and conversion paths
- SEO Audit: Evaluate technical SEO, keyword rankings, and backlink profile
- Content Inventory: Catalog existing content and its performance
- Social Media Assessment: Analyze engagement, growth, and sentiment across platforms
- Email Marketing Review: Examine list growth, open rates, click-through rates, and conversions
- Paid Media Evaluation: Review campaign performance, ROI, and targeting efficiency
Many free and paid tools can help with these audits, including Google Analytics, SEMrush, Ahrefs, and platform-specific analytics.
The goal is to identify what’s working and what isn’t, so you can make data-driven decisions about where to invest your resources.
Beginner Task: Perform a basic website audit using Google’s free tools like PageSpeed Insights and Mobile-Friendly Test. Make a list of three immediate improvements you can implement.
Advanced Task: Conduct a comprehensive competitive digital audit comparing your performance against 3-5 key competitors across all major channels. Identify strategic opportunities where competitors are underperforming.
Market Research & Customer Insights
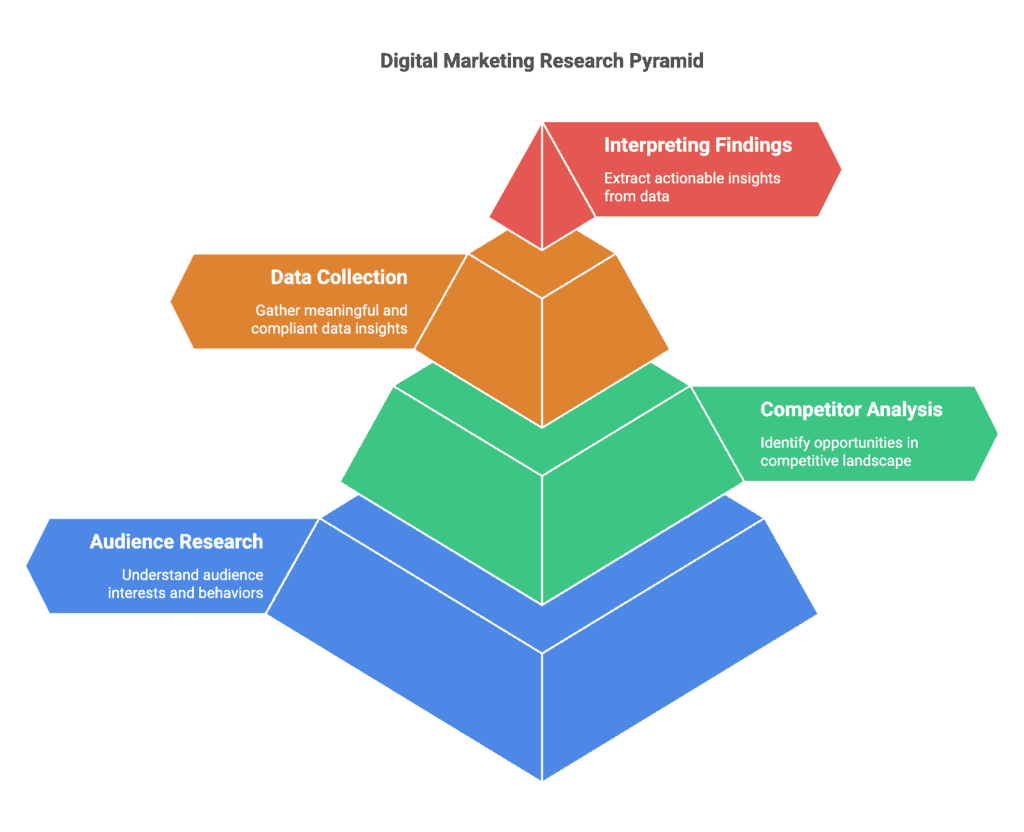
The most effective digital marketing strategies are built on deep customer understanding. Market research provides the insights you need to create relevant messaging and offers.
Without research, you’re just guessing about what your customers want and how to reach them.
Let’s explore the key components of effective digital market research.
Digital Audience Research Methods
Understanding who your audience is and what they care about is fundamental to effective marketing. Digital tools make audience research more accessible than ever before.
Effective research methods include:
- Analytics Data Analysis: Examine demographic and behavioral data from your website, social media, and email platforms
- Social Listening: Monitor conversations about your brand, competitors, and industry
- Surveys and Polls: Collect direct feedback through email, website, or social media surveys
- Interviews and Focus Groups: Gather qualitative insights through direct conversations
- User Testing: Observe how people interact with your digital properties
Look beyond basic demographics to understand psychographics – the attitudes, interests, and lifestyle factors that influence purchasing decisions.
Tools like Facebook Audience Insights, Google Analytics, and specialized platforms like SparkToro can reveal valuable information about your audience’s online behaviors and preferences.
Beginner Task: Use Google Analytics to identify your three most common audience segments by age, location, and device type. Create simple profiles for each.
Advanced Task: Develop detailed audience personas using both quantitative data and qualitative research. Include psychographic information, content preferences, digital behaviors, and purchase motivations.
Competitor Analysis Frameworks
Understanding your competitive landscape helps you identify opportunities and threats. Digital competitor analysis should go beyond simply monitoring what competitors post on social media.
A comprehensive competitor analysis includes:
- Digital Presence Mapping: Catalog all digital channels competitors use
- Content Strategy Analysis: Evaluate topics, formats, frequency, and engagement
- Keyword Gap Analysis: Identify keywords competitors rank for that you don’t
- Backlink Comparison: Analyze competitor backlink profiles and domain authority
- Positioning and Messaging Review: Compare how competitors communicate their value
- Product and Pricing Analysis: Examine how offerings are presented and priced online
Tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and SimilarWeb provide competitive intelligence that can inform your strategy.
Don’t just copy competitors – look for gaps and underserved needs you can address.
Beginner Task: Identify your three main competitors and complete a simple SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) for each based on their digital presence.
Advanced Task: Conduct a comprehensive content gap analysis to identify high-value topics your competitors are ranking for but you’re not addressing. Create a content plan to target these opportunities.
Data Collection Techniques
Good research relies on collecting the right data in the right ways. Digital marketers have numerous data collection options available.
Effective data collection techniques include:
- Web Analytics: Implement proper tracking to capture user behavior
- Heat Mapping: Visualize how users interact with your web pages
- Form Analysis: Track completion rates and abandonment points
- Conversion Funnels: Monitor how users move through purchase pathways
- Customer Feedback Tools: Implement NPS surveys and feedback widgets
- Session Recording: Review actual user sessions to identify pain points
When collecting data, always prioritize quality over quantity. A few meaningful insights are more valuable than mountains of irrelevant data.
Also, ensure your data collection is compliant with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA by obtaining proper consent and securing personal information.
Beginner Task: Implement Google Analytics on your website if you haven’t already, and set up at least three goals to track important user actions.
Advanced Task: Create a comprehensive data collection plan that integrates quantitative and qualitative methods. Include customer touchpoint mapping to identify key moments for gathering feedback.
Interpreting Research Findings
Collecting data is only half the battle. The real value comes from interpreting that data to extract actionable insights.
When analyzing your research:
- Look for Patterns: Identify recurring themes across different data sources
- Challenge Assumptions: Question whether the data supports or contradicts your expectations
- Segment Your Findings: Different audience segments may show different behaviors
- Prioritize Insights: Focus on findings that have the greatest strategic implications
- Translate to Action: Convert insights into specific recommendations
Effective interpretation often requires combining quantitative data (numbers and statistics) with qualitative insights (the “why” behind the numbers).
Present your findings in clear, visual formats that make it easy for stakeholders to understand the implications.
Beginner Task: Review your website analytics for the past month and write down three interesting patterns you notice about user behavior. For each pattern, note one action you could take in response.
Advanced Task: Create a research insights dashboard that connects key findings to strategic opportunities. Prioritize these opportunities based on potential impact and required resources.
Brand Framework & Messaging
A strong brand framework ensures consistency across all digital touchpoints. Without clear brand guidelines, your marketing can feel disjointed and confusing to customers.
Your brand is more than just your logo – it’s the total experience customers have with your business.
Let’s explore how to build and implement an effective brand framework.
Brand Guidelines Implementation
Brand guidelines provide the rules for how your brand should be presented across digital channels. Implementing these guidelines consistently builds recognition and trust.
Comprehensive brand guidelines typically include:
- Visual Elements: Logo usage, color palette, typography, and imagery style
- Voice and Tone: How your brand communicates in different contexts
- Brand Values: The core principles that guide your brand’s behavior
- Brand Story: The narrative that explains your brand’s purpose and history
- Application Examples: Practical examples of the guidelines in use
Digital-specific guidelines should also address website design, social media presentation, email templates, and digital advertising formats.
Make your guidelines accessible to everyone who creates content for your brand, including external partners and agencies.
Beginner Task: Create a simple one-page brand cheatsheet with your logo, primary colors (with hex codes), approved fonts, and 3-5 words that describe your brand voice.
Advanced Task: Develop comprehensive digital brand guidelines and conduct an audit of all your digital touchpoints to ensure consistent implementation. Create templates for common digital assets to facilitate consistency.
Voice, Tone, and Messaging Guidelines
How you say things is just as important as what you say. A distinctive and consistent voice helps your brand stand out in crowded digital spaces.
Effective voice and tone guidelines:
- Define Your Brand Voice: Establish 3-5 core voice attributes (e.g., “friendly but not casual” or “authoritative but not academic”)
- Differentiate Voice from Tone: Voice remains consistent while tone adapts to context and channel
- Include Examples: Show how your voice sounds in different situations
- Provide Do’s and Don’ts: Clear examples of appropriate and inappropriate communication
- Address Channel-Specific Considerations: How voice may vary slightly between email, social media, website, etc.
Your messaging guidelines should also include key messages for different audience segments and how to position your products or services.
Beginner Task: Write down three adjectives that describe your ideal brand voice, and create before/after examples showing how to transform generic text into content that reflects your voice.
Advanced Task: Create a comprehensive messaging architecture that includes your value proposition, supporting messages, proof points, and audience-specific variations. Test these messages with real customers to validate their effectiveness.
Storytelling & Brand Narrative Development
Stories create emotional connections with your audience. A compelling brand narrative provides context and meaning for your marketing messages.
Effective brand storytelling includes:
- Origin Story: How and why your business began
- Purpose Narrative: The problem you’re solving and why it matters
- Customer Success Stories: How real people benefit from your offering
- Brand Heritage: Your journey and evolution over time
- Future Vision: Where you’re headed and why customers should come along
Digital channels offer unique storytelling opportunities through multimedia content, interactive experiences, and community engagement.
The best brand stories are authentic, memorable, and consistently reinforced across touchpoints.
Beginner Task: Write a simple 100-word origin story for your business that highlights the problem you set out to solve and why it matters to customers.
Advanced Task: Develop a comprehensive brand narrative framework with modular storytelling elements that can be adapted for different channels and audience segments. Create a content calendar that systematically reinforces key narrative themes.
Message Testing & Refinement
Even the most carefully crafted messages need to be tested with real audiences. Digital channels make message testing faster and more cost-effective than ever before.
Effective message testing approaches include:
- A/B Testing: Compare two versions of website copy, email subjects, or ad headlines
- Social Media Polling: Gather quick feedback on messaging options
- User Testing: Observe how people react to different message framing
- Heat Mapping: See which messages capture attention and drive action
- Conversion Testing: Measure which messages drive desired behaviors
Look beyond surface metrics like clicks to understand how messages influence perception and behavior.
Use testing insights to continuously refine your messaging for maximum impact.
Beginner Task: Create two different versions of your homepage headline and run a simple A/B test to see which performs better. Use Google Optimize (free) to set this up.
Advanced Task: Implement a systematic message testing program that evaluates messaging effectiveness across channels and audience segments. Create a feedback loop where testing insights inform messaging strategy.
Customer Experience Foundation
Customer experience has become the primary competitive battleground in digital marketing. A thoughtful CX strategy creates loyal advocates who drive referrals and repeat business.
Digital touchpoints must be designed with the entire customer journey in mind.
Let’s explore how to build a strong customer experience foundation.
Buyer Persona Development
Buyer personas are semi-fictional representations of your ideal customers. They help you understand the specific needs, challenges, and motivations of different audience segments.
Effective buyer personas include:
- Demographics: Basic information like age, location, and job title
- Psychographics: Values, interests, and lifestyle factors
- Goals and Challenges: What they’re trying to achieve and what stands in the way
- Digital Behaviors: How they use technology and consume content
- Buying Process: How they research and make purchase decisions
- Objections: Common concerns that prevent purchase
The best personas are based on research, not assumptions. Use customer interviews, surveys, analytics, and sales team insights to build accurate profiles.
Most businesses have multiple personas, but start with the 2-3 most important segments to avoid complexity.
Beginner Task: Create a simple persona for your primary customer segment including basic demographics, top three goals, and top three pain points.
Advanced Task: Develop detailed personas for 3-5 key customer segments, including digital journey maps for each. Use these personas to audit your current content and identify gaps in addressing specific persona needs.
Customer Journey Mapping
A customer journey map visualizes the entire process customers go through when interacting with your brand. This tool helps identify opportunities to improve experience at critical touchpoints.
Comprehensive journey maps include:
- Stages: Awareness, consideration, decision, retention, advocacy
- Touchpoints: All interactions across digital and offline channels
- Actions: What customers do at each stage
- Thoughts and Feelings: Emotional responses throughout the journey
- Pain Points: Friction or frustration in the current experience
- Opportunities: Potential improvements to enhance the experience
Digital journey mapping should account for multiple entry points and non-linear paths that customers take.
Use journey maps to identify moments of truth – high-impact interactions that disproportionately influence customer perception.
Beginner Task: Sketch a simple five-stage journey map for your primary customer persona, listing the main touchpoints and one potential improvement for each stage.
Advanced Task: Create detailed journey maps for each key persona, incorporating actual customer feedback at each stage. Identify the highest-impact improvement opportunities and develop a prioritized roadmap for enhancing the customer experience.
Touchpoint Optimization
Each interaction a customer has with your brand is an opportunity to deliver value and strengthen the relationship. Optimizing these touchpoints improves conversion and satisfaction.
Key digital touchpoints to optimize include:
- Website Experience: Navigation, content, forms, and checkout process
- Search Experience: Both on-site search and SEO for external search
- Email Communications: From welcome series to transactional emails
- Social Media Interactions: Both proactive content and responsive engagement
- Customer Support: Self-service resources and direct assistance channels
- Mobile Experience: Apps and responsive web design
For each touchpoint, consider both functional performance (does it work efficiently?) and emotional impact (how does it make customers feel?).
Prioritize improvements based on touchpoint frequency and impact on customer decisions.
Beginner Task: Identify the three most important digital touchpoints for your business and conduct a simple audit of each. Note one improvement you could make to each touchpoint.
Advanced Task: Create a comprehensive touchpoint inventory with performance metrics for each. Implement a systematic optimization program starting with high-impact, high-friction points in the customer journey.
Experience Gap Analysis
Experience gaps occur when customer expectations don’t match the actual experience. Identifying and closing these gaps improves satisfaction and reduces churn.
Effective gap analysis includes:
- Expectation Mapping: Document what customers expect at each stage
- Experience Evaluation: Assess the reality of what customers actually experience
- Gap Identification: Pinpoint where expectations and reality don’t align
- Root Cause Analysis: Determine why gaps exist (technical issues, process problems, resource constraints)
- Prioritization: Focus on gaps with the highest impact on customer satisfaction
Tools like customer satisfaction surveys, NPS measurement, reviews analysis, and support ticket themes can help identify experience gaps.
Close gaps by either improving the experience to meet expectations or managing expectations to align with what you can realistically deliver.
Beginner Task: Survey 5-10 customers about their expectations for one key aspect of your digital experience, then compare their responses to the actual experience you provide. Identify one gap you can address immediately.
Advanced Task: Implement a systematic voice of customer (VOC) program that continuously monitors experience gaps across all stages of the customer journey. Create a cross-functional team responsible for addressing priority gaps.
Analytics & Measurement Infrastructure
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. A robust analytics infrastructure provides the insights needed to optimize your digital marketing strategy over time.
Effective measurement goes beyond basic traffic metrics to connect marketing activities with business outcomes.
Let’s explore how to build a strong analytics foundation.
Analytics Platform Setup
Proper analytics setup ensures you’re collecting accurate, comprehensive data about your digital marketing performance. Many businesses have analytics installed but not configured optimally.
A strong analytics foundation includes:
- Tool Selection: Choose platforms appropriate for your needs (Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, etc.)
- Proper Implementation: Correct tracking code installation and configuration
- Event Tracking: Capture important user interactions beyond pageviews
- Goal Configuration: Define and track meaningful conversion actions
- User ID Tracking: Connect user behavior across devices and sessions where appropriate
- Filter Setup: Exclude irrelevant traffic like internal users
- Custom Dimensions: Track additional data specific to your business
For most businesses, Google Analytics 4 provides a solid foundation that can be supplemented with specialized tools as needed.
Ensure your setup complies with privacy regulations by implementing proper consent management and data handling practices.
Beginner Task: Verify that your Google Analytics (or other analytics platform) is correctly installed and tracking pageviews. Set up at least three goals to track important conversion actions.
Advanced Task: Implement a comprehensive measurement plan that includes enhanced ecommerce tracking, custom dimensions for business-specific data, and cross-domain tracking if applicable. Set up server-side tracking to improve data accuracy in the face of ad blockers.
Key Performance Indicators Selection
KPIs translate your business objectives into measurable metrics. Selecting the right KPIs ensures you’re focusing on what truly matters rather than vanity metrics.
Effective KPI selection involves:
- Alignment with Objectives: Each business objective should have associated KPIs
- Outcome Focus: Emphasize results over activities (e.g., “revenue” over “posts published”)
- Balanced Scorecard: Include metrics for different aspects of performance
- Hierarchy: Create primary and supporting metrics for each objective
- Benchmarking: Establish realistic targets based on historical data and industry standards
- Attribution Consideration: Determine how to assign credit for conversions across channels
Common digital marketing KPIs include:
- Conversion rate
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
- Customer lifetime value (CLV)
- Return on ad spend (ROAS)
- Organic traffic growth
- Email engagement metrics
- Social media ROI
Beginner Task: For each of your main marketing objectives, identify one primary KPI and two supporting metrics. Set a specific target for each based on your current performance.
Advanced Task: Create a comprehensive KPI framework that connects top-level business objectives to channel-specific metrics. Implement a dashboard system that provides both executive summaries and detailed drill-down capability for marketing team members.
Custom Tracking Implementation
Standard analytics often doesn’t capture all the data you need. Custom tracking allows you to measure specific interactions important to your business.
Effective custom tracking includes:
- Custom Events: Track specific user interactions like video views, form interactions, or resource downloads
- Enhanced Ecommerce: Track detailed shopping behavior beyond basic transactions
- Custom Dimensions: Capture additional data like customer segments, content categories, or product attributes
- User ID Tracking: Connect user behavior across sessions and devices
- Campaign Tracking: Ensure all marketing efforts have proper UTM parameters
- Funnel Visualization: Track movement through conversion paths
- Scroll Depth Tracking: Measure content engagement beyond pageviews
Implementation options include Google Tag Manager, direct code implementation, or server-side tracking solutions.
Beginner Task: Set up Google Tag Manager on your site and implement at least three custom event tracking tags for important user interactions (like form submissions, button clicks, or video plays).
Advanced Task: Create a comprehensive tracking plan that documents all custom tracking needs, implementation methods, and data validation procedures. Implement server-side tracking to improve data reliability in the face of ad blockers and ITP restrictions.
Data Visualization Best Practices
Even the best data is useless if stakeholders can’t understand it. Effective data visualization transforms raw numbers into actionable insights.
Best practices for marketing data visualization include:
- Dashboard Design: Create role-specific views with appropriate detail levels
- Context Provision: Include benchmarks and targets for comparison
- Storytelling: Organize data to reveal meaningful patterns and trends
- Visual Hierarchy: Direct attention to the most important insights
- Simplification: Remove clutter and focus on what matters
- Consistent Updates: Refresh data at appropriate intervals
- Annotation: Add explanatory notes about significant changes or events
Tools like Google Data Studio, Tableau, Power BI, or even Excel can create effective visualizations.
The goal is not just to report what happened but to facilitate data-informed decision making.
Beginner Task: Create a simple one-page marketing dashboard using Google Data Studio (free) that shows your top 5-7 most important metrics in a clear, visual format.
Advanced Task: Develop a multi-level dashboard system with executive summaries, channel-specific dashboards, and campaign performance views. Implement automated anomaly detection to alert stakeholders to significant changes in key metrics.
Conclusion
Building a strong digital marketing strategy isn’t a one-time exercise – it’s an ongoing process of planning, execution, measurement, and refinement.
By mastering these fundamental elements, you’ll create a strategic foundation that guides all your tactical marketing decisions and maximizes your return on marketing investment.
The most successful digital marketers combine solid strategy with consistent execution and continuous learning. They stay focused on business objectives while remaining flexible enough to adapt to changing market conditions.
Now it’s your turn to take action. Start by assessing your current strategic foundation using the frameworks provided here. Identify the areas where you need the most improvement, and begin systematically strengthening your digital marketing strategy.
Remember, even small improvements to your strategic approach can yield significant results over time. The key is to start with clear objectives and a solid plan, then measure, learn, and adjust as you go.
What strategic element will you focus on improving first?