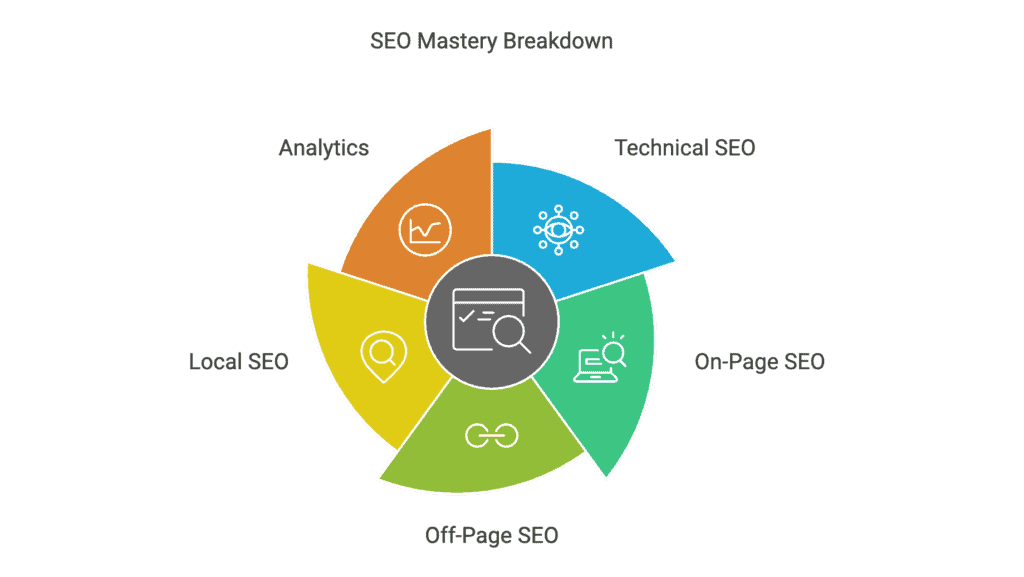
Are you struggling to get your website noticed online? Wondering why your competitors are ranking higher in search results? The answer lies in search engine optimization (SEO).
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn everything you need to know about SEO – from technical foundations to advanced strategies that drive real results.
- Learn the technical aspects that make your site search-engine friendly
- Master on-page optimization techniques that boost relevance
- Discover off-page strategies to build authority
- Implement local SEO tactics to dominate regional searches
- Set up proper analytics to track and improve performance
Technical SEO
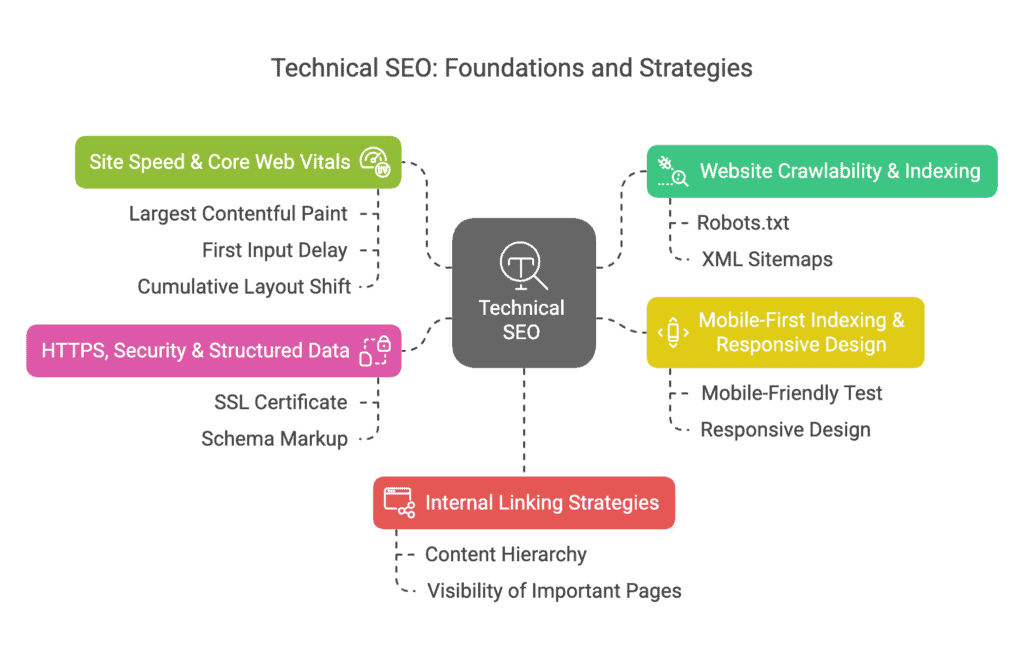
Technical SEO creates the foundation that allows search engines to properly crawl, index, and understand your website. Without a solid technical foundation, even the best content won’t rank.
- Website crawlability
- Site speed optimization
- Mobile-first indexing
- Security measures
- Internal linking strategies
Website Crawlability & Indexing (Robots.txt, XML Sitemaps)
Search engines can’t rank what they can’t find. That’s why ensuring your website is properly crawlable is the first critical step in any SEO strategy.
A robots.txt file tells search engines which pages they should and shouldn’t crawl. Think of it as a roadmap that guides search engine bots through your website.
XML sitemaps, on the other hand, provide a complete list of all your website’s important pages, ensuring that search engines discover and index your content efficiently.
Here’s why these elements matter:
- They help search engines find and understand your content
- They prevent important pages from being missed
- They can stop search engines from crawling duplicate or unimportant pages
- They provide critical information about your site structure
Beginner Task: Create a basic robots.txt file that allows all search engines to crawl your entire site, and generate a simple XML sitemap using a free online tool or WordPress plugin like Yoast SEO or Rank Math.
Advanced Task: Implement a dynamic XML sitemap that automatically updates when new content is published, and customize your robots.txt file to block crawling of parameter-based URLs, admin sections, and other low-value pages that might waste your crawl budget.
Site Speed & Core Web Vitals Optimization
In today’s fast-paced digital world, nobody likes waiting for slow websites. Google knows this, which is why site speed and user experience metrics (Core Web Vitals) have become critical ranking factors.
Core Web Vitals measure three key aspects of user experience:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How quickly the main content loads (should be under 2.5 seconds)
- First Input Delay (FID): How responsive your site is when users interact with it (should be under 100ms)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): How stable your layout is as the page loads (should be under 0.1)
Improving these metrics isn’t just good for SEO – it dramatically improves user experience, reduces bounce rates, and increases conversions.
Beginner Task: Run your website through Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool and implement the “easy wins” like image optimization, enabling browser caching, and removing unnecessary plugins or scripts.
Advanced Task: Implement advanced speed optimizations like critical CSS rendering, lazy loading of images and videos, and setting up a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to serve your content from servers closer to your users.
Mobile-First Indexing & Responsive Design
Google now predominantly uses the mobile version of your website for indexing and ranking. This means if your site doesn’t work well on mobile devices, your rankings will suffer – even for desktop searches.
Mobile-first indexing isn’t optional anymore. It’s essential.
Responsive design ensures your website adapts seamlessly to any screen size without sacrificing functionality or content. This creates a consistent experience across all devices.
Beginner Task: Test your website on Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool and address any issues it identifies. Also, browse your site on your smartphone to spot any usability problems.
Advanced Task: Implement Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) for key content pages or implement a progressive web app (PWA) approach for enhanced mobile performance while ensuring content parity between mobile and desktop versions.
HTTPS, Security & Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Security isn’t just about protecting your users – it’s a ranking factor. Google gives preference to secure websites that use HTTPS encryption.
Structured data (schema markup) helps search engines understand the context of your content, potentially leading to rich snippets in search results – those eye-catching listings with stars, images, and additional information.
Common schema types include:
- Review schema
- Recipe schema
- FAQ schema
- Product schema
- Local business schema
- Article schema
Beginner Task: Install an SSL certificate on your website (many hosting providers offer this for free) and test your site with Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to see if you’ve implemented any schema markup accidentally or through your theme.
Advanced Task: Implement structured data for your most important content types and create a security protocol that includes regular malware scans, strong password policies, and limited login attempts to protect against security breaches.
Internal Linking Strategies
Internal links are the unsung heroes of SEO. They help search engines discover and understand the relationship between different pages on your site while distributing link equity throughout your domain.
A strategic internal linking structure can:
- Establish content hierarchy
- Boost the visibility of important pages
- Enhance user navigation
- Reduce bounce rates
- Increase page views and time on site
Beginner Task: Identify your 5-10 most important pages and ensure they’re linked to from your homepage and main navigation. Also, start adding 3-5 relevant internal links to each new piece of content you create.
Advanced Task: Conduct a full internal link audit using a tool like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to identify orphaned pages, excessive links, and opportunities to implement a topic cluster model where you link related content to pillar pages.
On-Page SEO
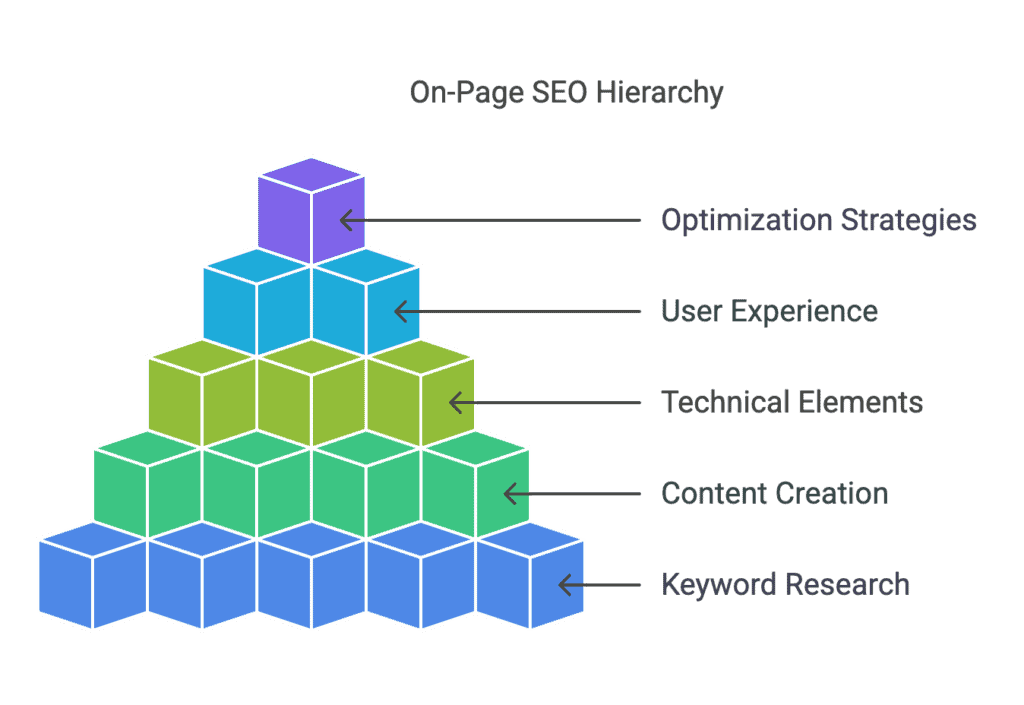
On-page SEO focuses on optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic. This involves both the content itself and the HTML source code.
- Keyword research
- Content creation and optimization
- Technical on-page elements
- User experience factors
Keyword Research & Intent Analysis
Effective SEO starts with understanding what your audience is searching for and why. Keyword research reveals these insights, helping you create content that matches user intent.
User intent generally falls into four categories:
- Informational: Looking for information (how to, what is, etc.)
- Navigational: Looking for a specific website
- Commercial: Researching products or services before buying
- Transactional: Ready to make a purchase
Targeting keywords without understanding intent leads to misaligned content that doesn’t satisfy users or search engines.
Beginner Task: Use free tools like Google Keyword Planner or Ubersuggest to identify 10-15 relevant keywords for your business with moderate search volume and low competition.
Advanced Task: Conduct comprehensive keyword research using tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz to build a content strategy that targets keywords at each stage of the buyer’s journey, clustered by topic relevance and mapped to specific pages on your site.
Publishing Keyword Rich Content
Content is still king in SEO, but not just any content – it needs to be comprehensive, valuable, and optimized for both users and search engines.
Creating content that ranks requires:
- Addressing the search intent completely
- Providing more value than competing content
- Natural incorporation of target and related keywords
- Proper formatting for readability
- Regular updates to maintain freshness
Beginner Task: Create a 1,000+ word article targeting one of your main keywords, making sure to include the keyword in the title, first paragraph, and at least one subheading while focusing primarily on providing valuable information.
Advanced Task: Develop a content calendar that addresses all your target keywords with a mix of content types (guides, case studies, infographics, videos) and implement a content refresh strategy to regularly update existing content with new information, examples, and statistics.
Content Clustering
Content clustering is an advanced SEO strategy that involves organizing your content into topical groups (clusters) around central “pillar” pages.
This approach:
- Creates semantic relationships between related content
- Establishes topical authority
- Improves internal linking structure
- Makes navigation more intuitive for users
- Helps search engines understand your site’s structure
Beginner Task: Identify one main topic relevant to your business and create a detailed pillar page about it, then plan 3-5 related subtopic articles that will link back to the pillar page.
Advanced Task: Map out a complete content cluster strategy for your website, with multiple pillar pages representing your core offerings, each supported by comprehensive clusters of subtopic content, all internally linked in a hub-and-spoke model.
Title Tags, Meta Descriptions & Header Optimization
These on-page elements are critical for both search engines and users:
- Title tags are the clickable headlines in search results
- Meta descriptions are the snippets that appear below the title
- Header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) structure your content hierarchically
Optimizing these elements improves click-through rates from search results and helps search engines understand your content’s structure and relevance.
Beginner Task: Audit your website’s homepage and five most important pages to ensure each has a unique title tag containing your target keyword, a compelling meta description, and properly structured header tags.
Advanced Task: Implement a systematic approach to title tag and meta description creation that includes modifiers based on intent (best, how to, review, etc.), emotional triggers, and calls to action, then test variations to improve click-through rates.
URL Structure & Best Practices
URLs might seem like a small detail, but they impact both SEO and user experience. A well-structured URL is:
- Descriptive but concise
- Keyword-rich when relevant
- Easy to read and understand
- Logical in its hierarchy
- Consistent in format
Beginner Task: Ensure all new content you create has clean, descriptive URLs that include your target keyword without unnecessary parameters or numbers.
Advanced Task: Audit your existing URLs to identify opportunities for improvement, implementing a strategic redirect plan for any URLs that need to be changed to maintain SEO value while improving structure.
Content Optimization (TF-IDF, NLP, EEAT)
Modern content optimization goes beyond keyword density to include semantic relevance, natural language processing, and Google’s EEAT principles (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness).
This advanced approach focuses on:
- Creating comprehensive content that covers all relevant aspects of a topic
- Using semantically related terms and entities
- Demonstrating expertise through accurate, detailed information
- Establishing trust through proper citations and credentials
- Providing a superior user experience with helpful formatting and media
Beginner Task: Enhance an existing article by bolding key points, adding relevant images or videos, breaking up text with subheadings, and including a “key takeaways” section at the end.
Advanced Task: Use TF-IDF analysis tools to identify semantically related terms missing from your content, implement schema markup to enhance E-E-A-T signals, and develop a content audit system that regularly evaluates existing content against competitive SERPs.
Image SEO & Accessibility
Images enhance user experience and provide additional ranking opportunities, but they need proper optimization:
- Descriptive file names
- Compressed file sizes
- Responsive sizing
- Meaningful alt text (for both SEO and accessibility)
- Appropriate image formats (JPEG, PNG, WebP)
Beginner Task: Optimize the images on your homepage by compressing them, adding descriptive alt text, and ensuring they display properly on mobile devices.
Advanced Task: Implement a comprehensive image optimization workflow that includes automated compression, responsive image delivery, lazy loading, WebP format conversion, and systematic alt text protocols that balance descriptiveness with keyword inclusion.
Off-Page SEO
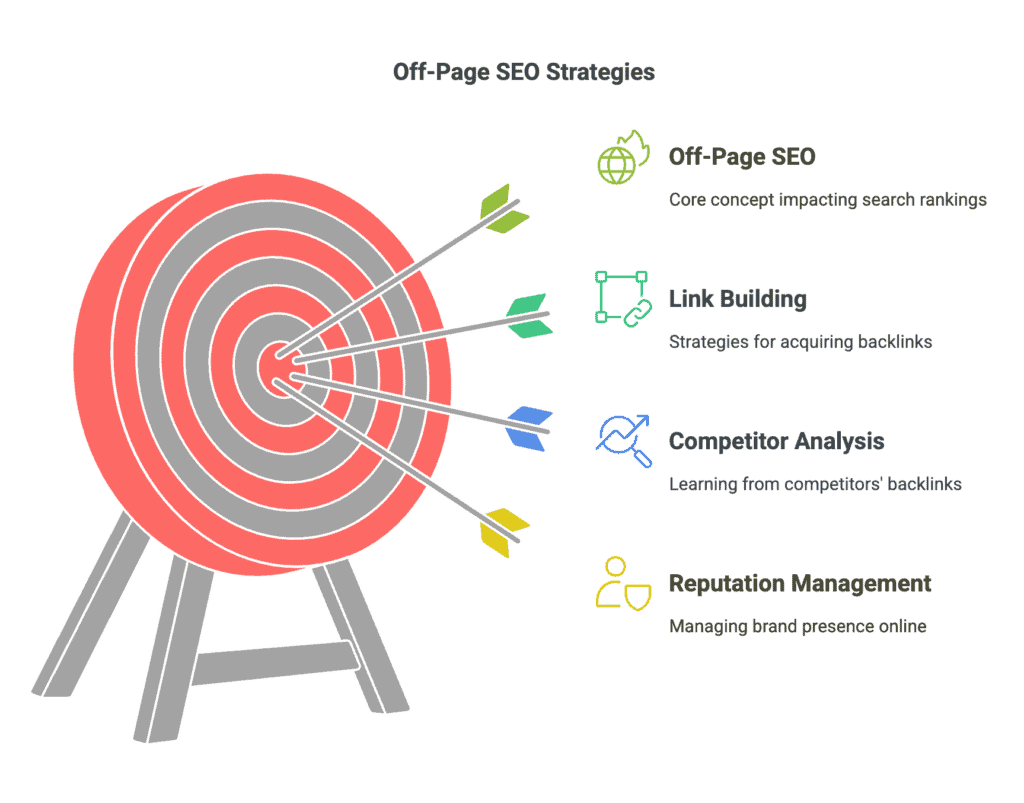
Off-page SEO refers to actions taken outside of your own website to impact your rankings within search engine results pages.
- Backlink acquisition
- Brand mentions and citations
- Social signals
- Content marketing
Link Building Strategies (Guest Posting, Digital PR, HARO)
Backlinks remain one of the most powerful ranking factors. They act as votes of confidence from other websites, signaling to search engines that your content is valuable and trustworthy.
Effective link building strategies include:
- Guest posting on relevant industry blogs
- Digital PR campaigns that generate news coverage
- HARO (Help A Reporter Out) to provide expert quotes
- Resource link building by creating valuable tools or guides
- Broken link building to replace dead links on other sites
Beginner Task: Create a list of 10 websites in your industry that accept guest posts, then pitch one with a helpful, non-promotional article idea that showcases your expertise.
Advanced Task: Develop a multi-faceted link building campaign that combines original research with digital PR outreach, HARO responses, and strategic content partnerships, tracking link acquisition costs and ROI.
Competitor Backlink Analysis & Reverse Engineering
Why start from scratch when you can learn from your competitors’ successes? Analyzing their backlink profiles reveals opportunities you can leverage.
This process involves:
- Identifying who links to your competitors
- Determining why they earned those links
- Finding gaps in their strategies
- Creating superior content to attract similar links
- Directly reaching out to the same referring domains
Beginner Task: Use a free tool like Moz’s Link Explorer to identify three top competitors and find their five most linked-to pages, then create better versions of that content for your own site.
Advanced Task: Conduct comprehensive competitor backlink analysis using premium tools to create a tiered outreach strategy targeting high-value referring domains, while developing content specifically designed to exploit gaps in competitor coverage.
Reputation Management & Brand Mentions
Brand mentions, even without links, contribute to your online reputation and may influence search rankings. Managing your brand’s online presence is crucial for both SEO and business success.
Effective reputation management includes:
- Monitoring brand mentions across the web
- Engaging with reviews and feedback
- Creating positive content that ranks for branded terms
- Addressing negative content constructively
- Building a consistent brand image across platforms
Beginner Task: Set up Google Alerts for your brand name and main product/service terms to monitor new mentions, and create a process for responding to reviews on Google Business Profile and other platforms.
Advanced Task: Implement a comprehensive online reputation management system that includes sentiment analysis, competitive brand monitoring, and strategic content creation to control the narrative around your brand in search results.
Local SEO
Local SEO focuses on optimizing your digital presence to attract more business from relevant local searches. For businesses with physical locations or serving specific geographic areas, local SEO is essential.
- Google Business Profile optimization
- Local content creation
- Citation management
- Review generation and monitoring
Introduction to Local SEO and How It Works
Local SEO differs from general SEO by focusing on location-specific factors. It’s designed to help businesses promote their products and services to local customers at the exact time they’re looking for them.
The local search algorithm considers:
- Relevance: How well your business matches what someone is searching for
- Distance: How far your location is from the searcher (or from the location specified in the search)
- Prominence: How well-known and reputable your business is
Beginner Task: Identify 5-10 location-specific keywords relevant to your business (e.g., “plumber in Chicago” or “best coffee shop downtown”) and make a list of your top local competitors.
Advanced Task: Conduct comprehensive local keyword research that includes neighborhood-specific terms, local landmarks, and long-tail phrases with local intent, then map these to specific pages and content opportunities on your website.
Setting Up and Optimizing Google Business Profile (GBP)
Your Google Business Profile is the cornerstone of local SEO. It influences your visibility in Google Maps, local pack results, and even standard organic search results.
Optimizing your GBP involves:
- Claiming and verifying your listing
- Selecting the correct business categories
- Adding complete and accurate business information
- Uploading high-quality photos and videos
- Creating Google Posts regularly
- Answering questions in the Q&A section
- Managing and responding to reviews
Beginner Task: Claim your Google Business Profile if you haven’t already, then complete every section of your profile, add at least 5 high-quality photos, and create your first Google Post.
Advanced Task: Develop a comprehensive GBP management strategy that includes weekly Google Posts, photo updates, Q&A monitoring, and using Google’s messaging feature, along with tracking insights to measure engagement and conversions from your listing.
On-Page Optimization for Local SEO
Local on-page optimization combines traditional SEO best practices with location-specific elements.
Key components include:
- Location-specific title tags and meta descriptions
- Local keywords in headings and content
- Location schema markup
- Embedded Google Maps
- Location-specific pages for multi-location businesses
- NAP (Name, Address, Phone) information in an easy-to-find location
Beginner Task: Optimize your website’s contact or about page with your full NAP information, embed a Google Map showing your location, and ensure your city and state appear in the title tag.
Advanced Task: Create location-specific landing pages for each service area or location you serve, with unique, valuable content about each area, properly structured schema markup, and area-specific testimonials and case studies.
Local Citations and NAP Consistency
Citations are mentions of your business NAP information on other websites. Consistency across all citations helps search engines verify your business information and improves local rankings.
Important citation sources include:
- Business directories
- Chamber of commerce websites
- Industry-specific platforms
- Social media profiles
- Review sites
Beginner Task: Ensure your business information is identical across your website, Google Business Profile, and Facebook page, then submit your information to three major directories like Yelp, Yellow Pages, and BBB.
Advanced Task: Conduct a citation audit to identify inconsistencies, duplicate listings, and opportunities for new citations, then use a citation management tool to systematically clean up and build your citation profile across general and industry-specific platforms.
Reviews and Reputation Management
Reviews directly influence both your local search rankings and whether customers choose your business. Managing your online reviews is critical for local SEO success.
Effective review management includes:
- Encouraging satisfied customers to leave reviews
- Monitoring reviews across platforms
- Responding promptly to all reviews, especially negative ones
- Addressing issues mentioned in negative reviews
- Highlighting positive reviews on your website
Beginner Task: Create a simple system for asking happy customers for reviews (like a follow-up email or text message), and make it a habit to respond to every new review within 24 hours.
Advanced Task: Implement a comprehensive review generation strategy with automated requests at optimal moments in the customer journey, review monitoring across all platforms, sentiment analysis of review content, and a crisis management protocol for handling negative feedback.
Local Link-Building Strategies
Local link building focuses on earning links from other businesses and organizations in your geographic area, which carry special weight for local search rankings.
Effective local link sources include:
- Local business associations
- Community sponsorships
- Local news websites and blogs
- Neighboring businesses
- Regional educational institutions
- Local events and charities
Beginner Task: Join your local chamber of commerce to earn a link from their member directory, and identify three local organizations you could sponsor or partner with to earn local links.
Advanced Task: Develop a community-focused content and outreach strategy that includes local event sponsorships, community resource guides, local scholarships, and collaborative content with non-competing local businesses.
SEO Analytics & Performance Tracking
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Tracking SEO performance is essential for understanding what’s working, what isn’t, and where to focus your efforts.
- Setting up proper tracking
- Interpreting performance data
- Measuring ROI
- Making data-driven decisions
Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides direct insights from Google about how they see and rank your website, making it an invaluable tool for SEO monitoring and troubleshooting.
Key features include:
- Performance reports showing clicks, impressions, CTR, and average position
- Index coverage issues and errors
- Mobile usability reports
- Core Web Vitals assessment
- Manual actions and security issues
- URL inspection tool
- Links report showing who links to you
Beginner Task: Set up Google Search Console for your website, verify ownership, and review the performance report to identify your top-performing pages and keywords.
Advanced Task: Implement regular Search Console audits that analyze clicks vs. impressions to find under-performing keywords, identify crawl errors and coverage issues, monitor mobile usability, and use the URL inspection tool to understand how Google sees your critical pages.
Rank Tracking & Competitor Benchmarking
Monitoring your search engine rankings and comparing them against competitors helps you understand your market position and track progress over time.
Effective rank tracking involves:
- Monitoring positions for target keywords
- Tracking ranking changes after website updates or algorithm changes
- Analyzing ranking performance by page type or topic
- Comparing rankings across different locations
- Benchmarking against key competitors
Beginner Task: Choose 10-15 of your most important keywords and record their current rankings using a free tool like Ubersuggest, then check them again in one month to track changes.
Advanced Task: Implement enterprise-level rank tracking for hundreds of keywords segmented by intent, search volume, and business value, with automated alerts for significant changes and competitive position analysis that identifies key ranking factors in your niche.
SEO Testing Tool and Reports
SEO testing involves making controlled changes to your website and measuring the impact on rankings, traffic, and conversions. This scientific approach leads to data-driven SEO decisions.
Common SEO tests include:
- Title tag variations
- Content format changes
- Internal linking adjustments
- Schema markup implementation
- UX and design modifications
Beginner Task: Create a simple spreadsheet to track key metrics (rankings, organic traffic, bounce rate) for your top 5 pages, then make one improvement to each page and document the results after 30 days.
Advanced Task: Implement a systematic SEO testing program using tools like SearchPilot or ClickFlow to run controlled A/B tests on title tags, meta descriptions, content length, and internal linking patterns, with proper statistical analysis of the results.
Conclusion
Search engine optimization isn’t a one-time task – it’s an ongoing process of improvement, adaptation, and growth. By mastering the technical foundation, creating optimized content, building authority through off-page tactics, implementing local strategies, and carefully tracking your results, you can achieve sustainable organic search success.
The most important thing is to start now and be consistent. Each improvement you make builds on the last, creating a compounding effect that can transform your online visibility and business results.
What one action will you take today to improve your SEO? The answer to that question could be the beginning of a transformation in your digital marketing results.